👋 Hi, it’s Rohit Malhotra and welcome to Partner Growth Newsletter, my bi-weekly newsletter doing deep dives into the fastest-growing startups and S1 briefs. Subscribe to join readers who get Partner Growth delivered to their inbox every Wednesday and Friday morning.
Latest posts
If you’re new, not yet a subscriber, or just plain missed it, here are some of our recent editions.
Subscribe to the Life Self Mastery podcast, which guides you on getting funding and allowing your business to grow rocketship.
Previous guests include Guy Kawasaki, Brad Feld, James Clear, Nick Huber, Shu Nyatta and 350+ incredible guests.
IPO Deep Dive
DoorDash in one minute
Founded by Tony Xu, Andy Fang, and Stanley Tang in 2013, DoorDash has grown into a leading force in U.S. food delivery. Unlike the traditional model, DoorDash has carved out a unique space with its decentralized approach, enlisting a network of independent contractors, or "Dashers," to fulfill delivery needs for a wide range of restaurants and local businesses. DoorDash’s mission is clear: to empower local economies and forge connections within communities.
DoorDash’s revenue strategy is anchored in commissions, subscriptions, and advertising services provided to its business partners. The company saw rapid expansion during the COVID-19 pandemic, becoming an essential service as demand for food delivery surged. By 2022, DoorDash reported revenues of $4.88 billion, marking a steady year-over-year increase. Despite record-breaking orders that hit 426 million in Q3 2022, profitability remains elusive, with the company reporting a net loss of $468 million in its most recent fiscal year.
For a deep dive into DoorDash’s vision, how it reshaped gig work in food delivery, and the competitive landscape it navigates, keep reading.
Introduction
DoorDash (DASH) Stock Overview
Current Price: $155.60 (as of market close)
Market Cap: $64.04B
52-Week Range: $72.65 - 155.90
EPS (TTM): -1.01
While DoorDash’s journey has been marked by rapid growth, its valuation remains a testament to fierce competition in food delivery and a rollercoaster economy. Yet DoorDash's story reaches beyond mere delivery—it's about reshaping access to local goods. CEO Tony Xu sees DoorDash evolving into a core logistics network for local commerce, a mission that resonated when the company went public in December 2020, debuting at $102 per share and soaring to $189.51 on its first day.
Recent Developments
DoorDash’s growth has paralleled the digital wave sweeping the service industry, with demand surging through the pandemic and beyond. CEO Tony Xu often outlines DoorDash’s vision of becoming a “logistics platform for local commerce,” extending its reach into grocery and convenience store deliveries. No longer confined to restaurants, DoorDash now collaborates with over 500,000 merchants, strengthening customer loyalty through its “DashPass” subscription program.
In the face of competition from Uber Eats and Grubhub, DoorDash has diversified its revenue model, leveraging partnerships and white-label services like “DoorDash Drive.” However, fierce competition and escalating costs have challenged profitability, prompting a sharp focus on efficiency. Recent innovations, like “DoubleDash”—which allows customers to add items from nearby merchants to their original order—aim to enhance order value and deliver greater convenience to users.
Investor Sentiment
t wasn’t the beginning of the end for DoorDash, though some argue it might have been. To bullish investors, DoorDash stands as a powerhouse in the on-demand logistics space. “We’re not just about delivering food,” CEO Tony Xu suggests. Instead, DoorDash aims to redefine local commerce, reaching beyond restaurant delivery into areas like grocery and convenience, with DashPass subscriptions building a recurring customer base. Gross order value continues to climb, reflecting DoorDash’s growing importance to merchants and consumers alike.
And yet, others are less optimistic. Bearish investors see in DoorDash a familiar story of high-spending, low-margin struggles. “Can DoorDash sustain this model?” they ask, eyeing the company’s heavy losses and reliance on promotions to drive growth. Competition from Uber Eats and Grubhub remains fierce, and as regulatory pressure on gig economy labor models mounts, DoorDash’s reliance on its decentralized network of Dashers could face significant cost pressures.
In DoorDash’s journey, the central question looms: can it turn a profit while retaining its lead in an industry where competition is cutthroat, and the regulatory landscape grows ever more complex?
History
DoorDash’s journey began in 2013 when four Stanford students—Tony Xu, Stanley Tang, Andy Fang, and Evan Moore—set out to tackle a crucial issue: the lack of reliable last-mile delivery for local businesses. What started as a simple service called “Palo Alto Delivery” quickly evolved. Recognizing a greater need in underserved suburban markets, the team rebranded to DoorDash, positioning itself as the delivery solution for communities with limited options.
Fast forward to 2020, and DoorDash had transformed from a small startup into a market leader, claiming 50% of the U.S. food delivery space. With a network encompassing 390,000 merchants, 18 million customers, and 1 million Dashers, DoorDash had become more than a delivery service—it emerged as a robust logistics platform driving connections between local businesses and their communities.
Market Opportunity
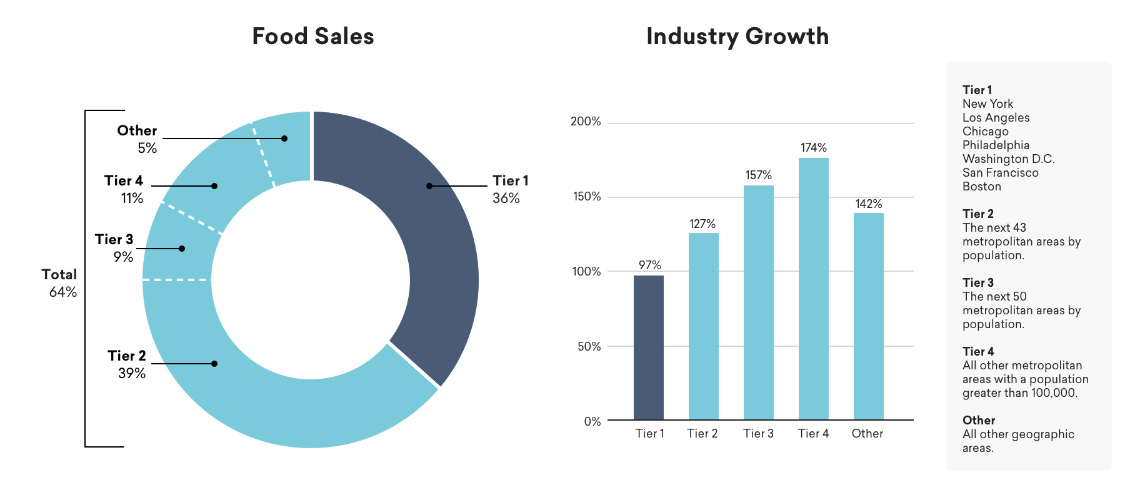
DoorDash’s market extends far beyond restaurants. As of 2019, U.S. consumers spent $1.5 trillion on food and beverages, with $600.5 billion allocated to restaurant services. DoorDash zeroed in on the $302.6 billion off-premise dining market (including takeout and delivery), capturing $8 billion in Gross Order Volume (GOV) in 2019, reflecting less than 3% of the total off-premise spend—a signal of its massive growth potential.
The pandemic accelerated DoorDash’s expansion into non-food sectors like groceries, convenience, and pharmaceuticals, tapping into a growing need for on-demand delivery of essential goods. According to estimates, these new verticals are expected to contribute to a market valued at over $100 billion by 2025. With an expansive logistics infrastructure, DoorDash is primed to capture a significant share of this opportunity, positioning itself not just as a food delivery service but as an all-encompassing logistics solution.
Product Overview
DoorDash’s product offerings are structured to serve three main groups: consumers, merchants, and Dashers. Each component is crafted to maximize convenience and utility, driving value across the ecosystem.
Marketplace: The primary platform connects consumers to local restaurants for delivery or pickup. In 2020, the DoorDash Marketplace generated $1.9 billion in revenue and powered the growth of same-store sales for merchants by 59% year-over-year. DoorDash’s network offers access to over 390,000 merchants, including small local businesses and national chains like McDonald’s and Taco Bell.
DashPass: This popular subscription model, priced at $9.99 per month, offers unlimited free deliveries from eligible restaurants. DashPass attracted 5 million subscribers by the end of 2020, with members ordering nearly three times more than non-subscribers. This recurring revenue stream is a crucial component of DoorDash’s long-term growth strategy.
Drive: Drive is DoorDash’s white-label delivery service, allowing other companies to leverage DoorDash’s logistics for their own branded experiences. By partnering with grocers, retailers, and other non-food merchants, Drive has quickly become a critical revenue stream, extending DoorDash’s reach into a projected $100 billion non-food delivery market.
Business Model:
DoorDash’s revenue model is carefully structured to support growth across multiple channels, while providing flexibility for merchants and value for consumers.
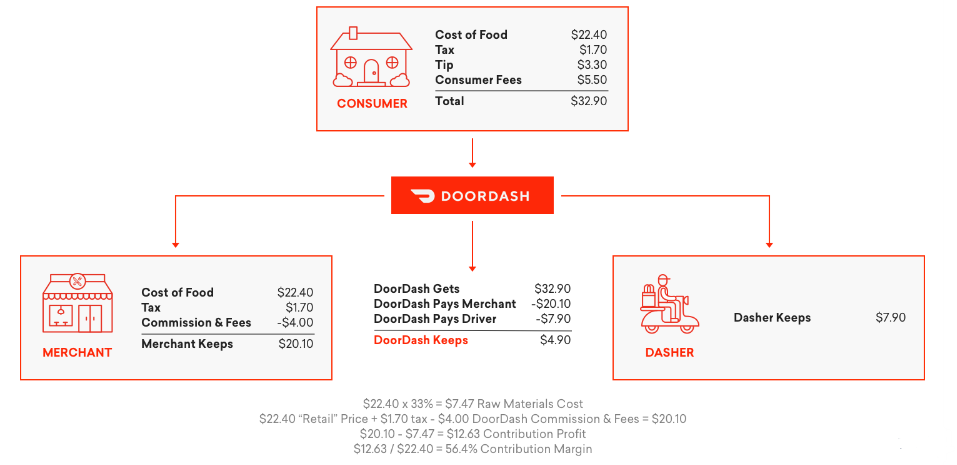
Commission Fees: Merchants on DoorDash’s Marketplace are charged a commission fee, typically ranging from 15% to 30% of each order’s value. During the pandemic, DoorDash introduced a tiered commission structure to better support small businesses, with the higher rates linked to enhanced marketing and promotional features.
Delivery and Service Fees: Delivery fees vary based on order distance and restaurant type, with an average of around $5 per order for non-DashPass members. The DashPass subscription, on the other hand, reduces per-order fees for loyal customers, boosting order frequency.
Subscription Revenue: DashPass brings in recurring monthly revenue and fosters loyalty. With subscribers ordering up to 3x more frequently than non-subscribers, DashPass has become an essential tool for increasing GOV and user retention.
Drive Revenue: Drive allows businesses to utilize DoorDash’s delivery network for orders placed through their own platforms. By 2020, this service expanded DoorDash’s GOV well beyond restaurant delivery, capturing demand from sectors such as grocery and retail.
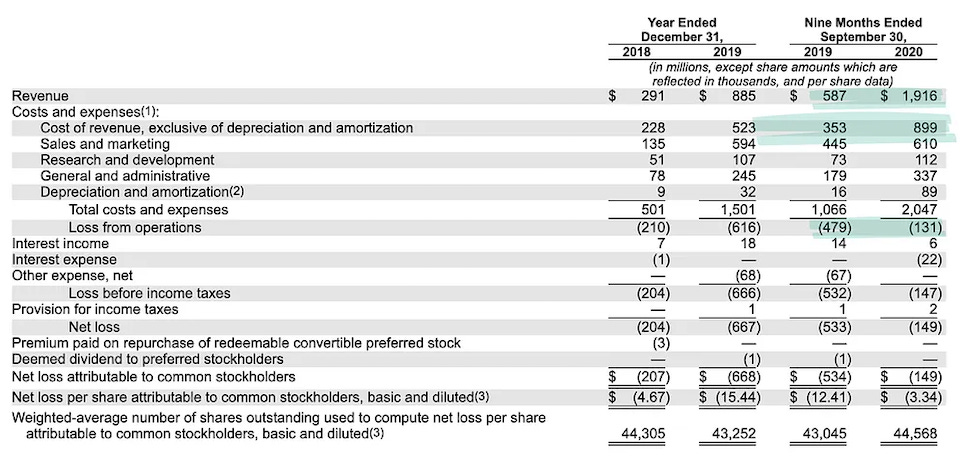
This diversified revenue model has enabled DoorDash to generate $1.9 billion in revenue by Q3 2020, a significant leap from $885 million in 2019. The flexibility of its revenue channels has made it possible to maintain high GOV while reaching into emerging verticals.
Management Team:
DoorDash’s leadership team combines operational expertise with a clear vision for the future, driving the company’s rapid scale-up:
Tony Xu (CEO): An immigrant from China, Xu’s early experiences watching his mother work in a restaurant gave him insight into the struggles of small business owners. Under his leadership, DoorDash has grown into a logistics juggernaut, focused on empowering local economies.
Andy Fang (CTO) and Stanley Tang (CPO): Co-founders Fang and Tang have led DoorDash’s tech and product divisions, respectively. Fang oversees the platform’s core technology, while Tang, as Head of DoorDash Labs, explores future tech and logistical innovations.
Prabir Adarkar (CFO): Formerly with Uber, Adarkar brings extensive experience in scaling operations and achieving financial stability. His expertise is central to DoorDash’s goal of balancing growth with profitability.
The management team’s collective expertise has been key to DoorDash’s success, especially during periods of rapid expansion. The leadership’s emphasis on a “merchant-first” approach has shaped the company’s values and positioned it as a reliable partner for local businesses.
Investor and Ownership Structure:
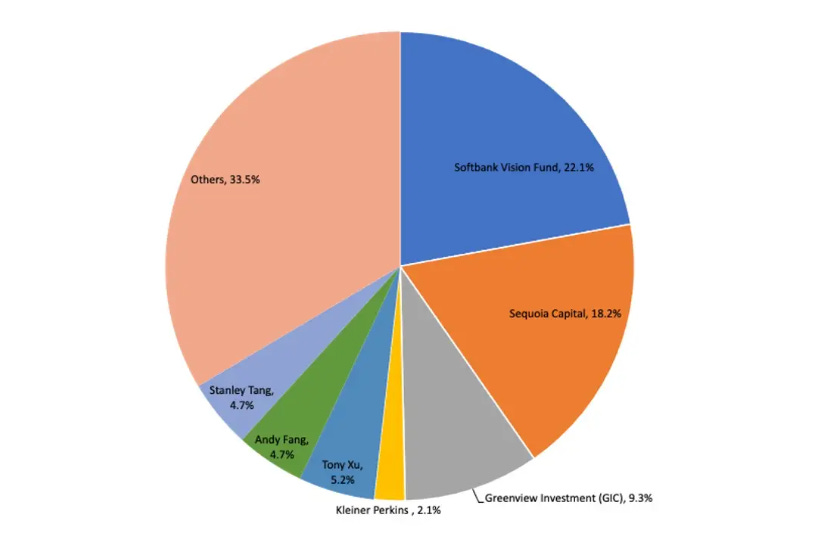
DoorDash completed their IPO on December 9, 2020 to list on NYSE with ticker DASH at an implied valuation of $32.4B.Key investors, including SoftBank Vision Fund, Sequoia Capital, and Khosla Ventures, have been instrumental in funding DoorDash’s aggressive expansion.
Funding History: DoorDash’s Path to Success
1. Series A (September 2013)
Amount Raised: $19.7 million
Raised to Date: $19.7 million
Issue Price: $0.73
Post-Money Valuation: $12.25 million
Key Investors: Khosla Ventures, Charles River Ventures, Haystack, SV Angel, YCombinator
2. Series A-1 (May 2014)
Amount Raised: $2 million
Raised to Date: $21.7 million
Issue Price: $0.15
Post-Money Valuation: $72.85 million
Key Investors: Sequoia Capital, Khosla Ventures, Charles River Ventures
3. Series B (March 2015)
Amount Raised: $45 million
Raised to Date: $66.7 million
Issue Price: $5.68
Post-Money Valuation: $598.75 million
Key Investors: Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers, Charles River Ventures, Khosla Ventures, Pejman Mar Ventures, Sequoia Capital
4. Series C (March 2016)
Amount Raised: $128.5 million
Raised to Date: $195.2 million
Issue Price: $4.79
Post-Money Valuation: $692.1 million
Key Investors: Sequoia Capital, Y Combinator, Khosla Ventures, Wellcome Trust, Kleiner Perkins Caufield Byers
5. Series D (March 2018)
Amount Raised: $539.72 million
Raised to Date: $734.92 million
Issue Price: $5.51
Post-Money Valuation: $1.46 billion
Key Investors: GIC Private, Sequoia Capital, SoftBank Group, Wellcome Trust
6. Series E (August 2018)
Amount Raised: $250 million
Raised to Date: $984.92 million
Issue Price: $13.85
Post-Money Valuation: $4.38 billion
Key Investors: DST Global, Coatue Management, SoftBank Group, Khosla Ventures, Charles River Ventures, Sequoia Capital, Kleiner Perkins
7. Series F (February 2019)
Amount Raised: $408.73 million
Raised to Date: $1.39 billion
Issue Price: $22.48
Post-Money Valuation: $7.14 billion
Key Investors: Coatue Management, Dragoneer Investment Group, DST Global, GIC Private, Sequoia Capital, Softbank Group, Temasek Holdings, Y Combinator
8. Series G (May 2019)
Amount Raised: $600 million
Raised to Date: $1.99 billion
Issue Price: $37.94
Post-Money Valuation: $12.62 billion
Key Investors: Coatue Management, Darsana Capital Partners, Dragoneer Investment Group, DST Global, Sands Capital Ventures, Sequoia Capital, SoftBank Group, Temasek Holdings
9. Series H (June 2020)
Amount Raised: $429.25 million
Raised to Date: $2.42 billion
Issue Price: $45.91
Post-Money Valuation: $16.08 billion
Key Investors: Dragoneer Investment Group, Durable Capital Partners, Fidelity Investments, PV Seed Fund, T. Rowe Price
Competition
The U.S. food delivery sector is highly competitive, with DoorDash facing off against Uber Eats, Grubhub, and smaller players like Postmates. However, DoorDash’s focus on suburban markets—where it holds 58% of the market share—has been instrumental in establishing dominance in regions overlooked by urban-focused competitors.
DoorDash’s expansion into non-food sectors puts it in competition with Instacart and Amazon, two logistics giants with significant market influence. The company’s emphasis on multi-vertical expansion, combined with its strength in suburban markets, positions it to continue outpacing rivals while capturing an increasing share of consumer spending.
Financials
DoorDash’s financial performance showcases the tension between rapid growth and profitability:
2018: Revenue was $291 million, with a net loss of $679 million as the company focused on scaling operations.
2019: Revenue increased to $885 million, while net losses fell slightly to $667 million.
2020 (Q3 YTD): Revenue surged to $1.9 billion, narrowing net losses to $149 million.
DoorDash's financial performance has been remarkable, and it's evident that COVID-19 has accelerated the company’s growth trajectory, with revenue for the June 2020 quarter surging by 86% quarter-over-quarter. While there has been widespread skepticism regarding the sustainability of the on-demand economy—especially given the ongoing cash burn seen in companies like Uber and Lyft—DoorDash has demonstrated a different path. In the nine months leading up to September 2020, the company achieved positive cash flow from operating activities and even reported a quarter of GAAP operating income in June 2020. DoorDash has shown that its business model is not only sustainable but also capable of delivering robust growth, healthy margins, and strong cash flows in the future.
Quarterly Revenue ($M) and Take Rate (% of GOV):
This chart showcases quarterly revenue growth, peaking at $879M in Sep-20, with the take rate stabilizing around 12%. The year-over-year (YoY) growth of 268% highlights significant acceleration.
Quarterly Revenue Run-Rate & Implied Net New Revenue Run-Rate ($M):
The graph tracks revenue run-rate expansion, reaching $3.5B by Sep-20. Spikes in net new revenue, especially in Jun-20 and Sep-20, reflect substantial new business inflows post-pandemic.
Quarterly Gross Order Volume (GOV) ($M):
This chart illustrates the steady rise in gross order volume, surging from $3.1B in Mar-20 to $7.25B in Sep-20, driven by 246% YoY growth.
Cash Flows ($M): This chart shows DoorDash's cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities from 2018 to September 2020. DoorDash had $1.6 billion in cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities as of the latest data.
GAAP and Non-GAAP Operating and Contribution Margins: This chart illustrates DoorDash's improvements in GAAP and non-GAAP operating margins, along with contribution margin growth, showing a shift from deep losses to near break-even levels by Q3 2020.
Quarterly Non-GAAP Gross Margin and Operating Expenses as a % of Revenue: DoorDash's gross margin rose steadily, reaching 57% by Q3 2020, while sales and marketing expenses as a percentage of revenue declined, indicating increasing operational efficiency.
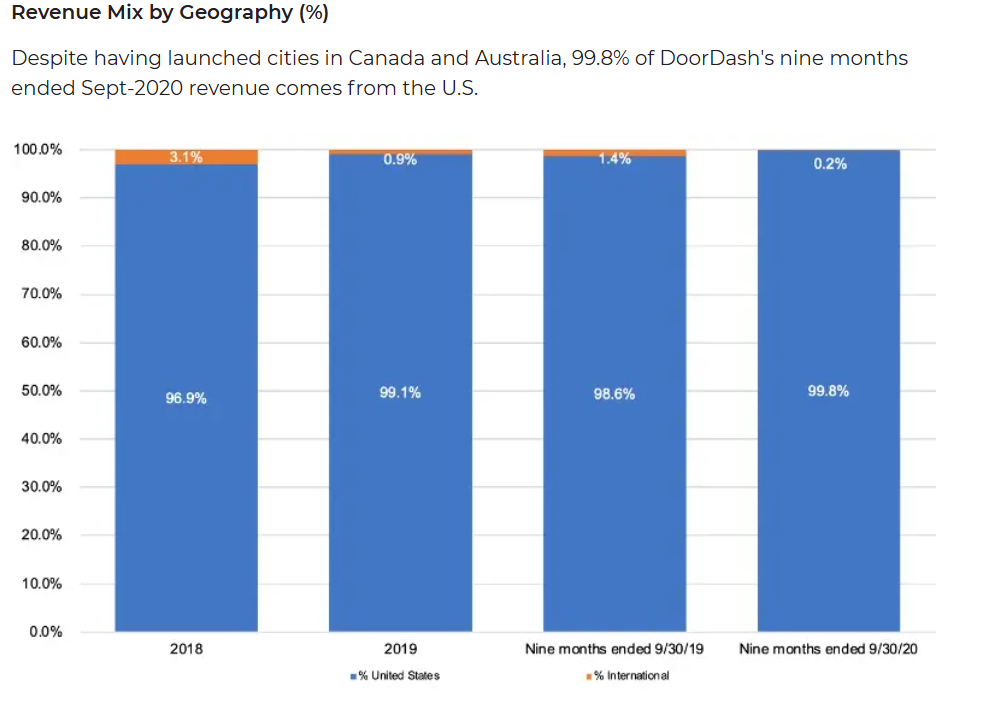
Revenue Mix by Geography (%): This chart highlights DoorDash's heavy reliance on the U.S. market, with 99.8% of its revenue in the nine months ending September 2020 coming from the United States, despite expansions into Canada and Australia.
DoorDash’s substantial growth in Gross Order Volume (GOV) and its cost optimization efforts have improved gross margins and Contribution Profit, demonstrating the potential for profitability. Its strategic focus on operational efficiency, particularly within logistics, and the higher customer retention driven by DashPass show a path forward toward sustainable profit margins.
Closing thoughts
DoorDash’s journey exemplifies the transformation of a modest delivery service into a leader in on-demand logistics, a shift that mirrors broader trends in digital adoption. What began in 2013 with four Stanford students determined to solve last-mile delivery challenges evolved into a platform that connects over 500,000 merchants to 18 million consumers, supported by a decentralized network of Dashers. This innovative model carved out a unique position for DoorDash in an increasingly competitive market, differentiating it through its focus on empowering local economies and fostering connections within communities.
Throughout its growth, DoorDash has continuously adapted to meet consumer demands, from food delivery to grocery and convenience options, reflecting a vision of becoming a full-service logistics platform for local commerce. Despite challenges like fierce competition from Uber Eats and Grubhub and regulatory scrutiny on gig economy models, DoorDash has maintained growth by diversifying its revenue streams and expanding into non-food sectors. Key offerings such as DashPass, Drive, and DoubleDash underscore DoorDash's commitment to convenience and loyalty, driving significant engagement and a higher average order value.
However, DoorDash’s rapid ascent has not come without costs. With substantial operating losses and increased spending on customer acquisition, the company faces the ongoing challenge of achieving sustainable profitability. While DoorDash has shown progress in operational efficiency and cash flow management, questions remain about the sustainability of its high-spending model amid rising labor costs and regulatory pressures.
As DoorDash moves forward, it aims to balance growth with profitability, capturing opportunities in a multi-billion dollar logistics market. Its path remains closely watched by investors and competitors alike, as DoorDash navigates the complex landscape of on-demand services with the potential to become a cornerstone of local commerce.
If you enjoyed our analysis, we’d very much appreciate you sharing with a friend.
Tweets of the week
Cold emails > referrals!
Hopefully, more public CEOs follow this!
Here are the options I have for us to work together. If any of them are interesting to you - hit me up!
Get my free sales course: Click here to receive a 5-day educational email course on how to get high-ticket enterprise clients
Subscribe to my YouTube channel: Your Learning Playground with over 350+ podcasts. Previous guests include Guy Kawasaki, Brad Feld, James Clear, and Shu Nyatta.
Sponsor this newsletter: Reach thousands of tech leaders
And that’s it from me. See you on Friday.
What do you think about my bi-weekly Newsletter? Love it | Okay-ish | Stop it